Cardiac Muscle Branching. When one cardiac muscle cell is stimulated to contract a gap junction transfers the stimulation to the next cardiac cell. Cardiac muscles function solely for pumping blood away from the heart towards the lungs and throughout the body.
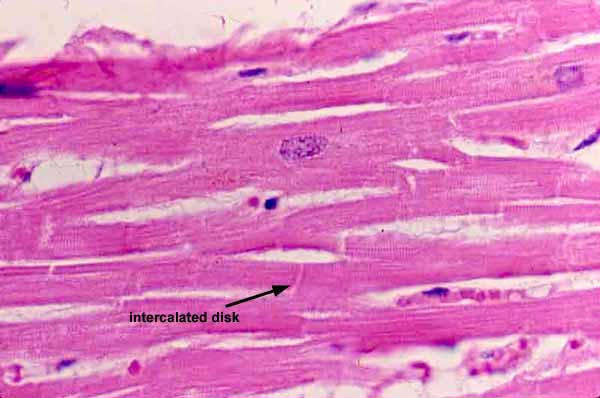
However cardiac muscle has a number of notable histological differences including. Unique to the cardiac muscle are a branching morphology and the presence of intercalated discs found between muscle fibers. Like skeletal muscle cardiac muscle cells are striated due to a similar arrangement of contractile proteins.
An intercalated disc allows the cardiac muscle cells to contract in a wave-like pattern so that the heart can work as a pump.
While each cell is not very strong by itself millions of cardiac muscle cells working together are easily able to pump all of the blood in the body through the heart in less than a minute. Cardiac muscle cells contain larger amounts of mitochondria than other cells. They are often seen as zigzagging bands cutting across the muscle fibers. The muscle that contains cylindrical cells with branching ends is the cardiac muscle.
